这篇文章主要介绍了30分钟用Node.js构建一个API服务器的步骤详解,小编觉得挺不错的,现在分享给大家,也给大家做个参考。一起跟随小编过来看看吧
Node.js 对初学者来说可能是令人望而却步的,其灵活的结构和缺乏严格的规范使它看起来很复杂。
本教程是 Node.js,Express 框架和 MongoDB 的快速指南,重点介绍基本的 REST 路由和基本的数据库交互。你将构建一个简单的 API 框架模版,然后可以将其用作任何应用。
本教程适用于:你应该对 REST API 和 CRUD 操作有基本的了解,还有基本的 JavaScript 知识。我用的是 ES6(主要是箭头函数),但并不是很复杂。
在本教程中,我们将为创建一个网络笔记应用的后端骨架 ―― 类似于Google Keep,能够执行所有的四个CRUD操作:创建、读取、更新和删除。
配置
如果你没有安装Node,请参阅此处。
创建一个新目录,运行 npm init,然后按照提示操作,把你的应用程序命名为“notable”(或者你可能喜欢的其他名字)。
npm init
一旦完成,在你的目录中会有一个 package.json 文件。你可以开始安装项目所需的依赖项了。
我们将使用 Express 作为自己的框架,MongoDB 作为数据库,还有一个名为 body-parser 的包来帮助处理 JSON 请求。
npm install --save express mongodb@2.2.16 body-parser
我还强烈建议将 Nodemon 安装为 dev 依赖项。这是一个非常简单的小包,可在文件被更改时自动重启服务器。
如果你运行:
npm install --save-dev nodemon
然后将以下脚本添加到 package.json:
// package.json "scripts": { "dev": "nodemon server.js" },完整的 package.json 应如下所示:
// package.json { "name": "notable", "version": "1.0.0", "description": "", "main": "server.js", "scripts": { "dev": "nodemon server.js" }, "author": "", "license": "ISC", "dependencies": { "body-parser": "^1.15.2", "express": "^4.14.0", "mongodb": "^2.2.16" }, "devDependencies": { "nodemon": "^1.11.0" } }现在,你可以创建 server.js 文件并构建 API 了。
我们的服务器
首先导入 server.js 中的所有依赖项。
// server.js const express = require('express'); const MongoClient = require('mongodb').MongoClient; const bodyParser = require('body-parser'); const app = express();我们将使用 MongoClient 与数据库进行交互。还会将应用初始化为 Express 框架的实例。
最后一件事就是告诉你的程序开始监听请求。
你可以指定一个端口,并像这样开始监听:
// server.js const port = 8000; app.listen(port, () => { console.log('We are live on ' + port); });现在,如果你运行 npm run dev(或 node server.js,如果你没有安装 Nodemon 的话),应该在终端中看到“We are live on port 8000”的提示。
你的服务器已经启动了。但它现在还什么也做不了。
接下来让我们解决这个问题。
CRUD 路由
对于本例,你要构建4条路由; 创建笔记,阅读笔记,更新笔记和删除笔记。
这将使你了解如何使用 Node 构建几乎所有的基本路由。
但是,要测试你的API,还需要模仿客户端发出请求。为此,我们将使用名为 Postman 的优秀应用。它允许你使用自定义的头和参数进行简单的 HTTP 请求。
安装Postman,让我们开始设置路由。
项目结构
大多数 Node.js 教程(以及许多真实的案例)都将所有路由放在一个很大的 routes.js 文件中。这让我有点不舒服。相比之下,将文件拆到为单独的文件夹可以提高可读性,并使大型应用更易于管理。
虽然我们现在做的不是大型应用,但仍然可以这样做。创建以下目录:一个 app 文件夹,里面有一个routes文件夹,routes 里面有 index.js 和 note_routes.js 文件。
mkdir app cd app mkdir routes cd routes touch index.js touch note_routes.js
对于你的简单小程序来说,这些目录可能看起来有些过分,但从一开始就做好总是有意义的。
你的第一个路由
让我们从 CRUD 中的 C 开始。你将会如何创建一个笔记?
那么,在你开始之前,必须先要打好基础。在Express中,路由包含在一个函数中,该函数将 Express 实例和数据库作为参数。
像这样:
// routes/note_routes.js module.exports = function(app, db) { };然后,你可以通过 index.js 导出此函数:
// routes/index.js const noteRoutes = require('./note_routes'); module.exports = function(app, db) { noteRoutes(app, db); // Other route groups could go here, in the future };然后导入它以便在 server.js 中使用:
// server.js const express = require('express'); const MongoClient = require('mongodb').MongoClient; const bodyParser = require('body-parser'); const app = express(); const port = 8000; require('./app/routes')(app, {}); app.listen(port, () => { console.log('We are live on ' + port); });请注意,由于还没有设置数据库,因此只需传入一个空对象。
好的,现在你可以制作自己的 CREATE 路由了。
语法很简单:
// note_routes.js module.exports = function(app, db) { app.post('/notes', (req, res) => { // You'll create your note here. res.send('Hello') }); };当应用程序收到对 '/ notes' 路径的 post 请求时,它将执行回调内的代码 ―― request 对象(包含请求的参数或JSON)和 response 对象。
你可以使用 Postman 将 POST 请求发送到 localhost:8000/notes 来测试。

你应该得到回复:'Hello'。
太好了!你创建了第一个真正的路由。
下一步是在你的请求中添加一些参数并在 API 中处理它们,最后添加到你的数据库中。
请求参数
在 Postman 中,在选择 x-www-form-urlencoded 单选按钮后,转到 Body 选项卡并添加一些键值对。
这会将编码后的表单数据添加到你的请求中,你可以使用 API 处理该请求。

你可以去尝试更多的设置项。
现在在你的 note_routes.js 中,让我们输出 body 的内容。
// note_routes.js module.exports = function(app, db) { app.post('/notes', (req, res) => { console.log(req.body) res.send('Hello') }); };用 Postman 发送请求,你会看到……undefined。
不幸的是,Express 无法自行处理 URL 编码的表单。虽然你确实安装了这个 body-parser 包......
// server. const express = require('express'); const MongoClient = require('mongodb').MongoClient; const bodyParser = require('body-parser'); const app = express(); const port = 8000; app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({ extended: true })); require('./app/routes')(app, {}); app.listen(port, () => { console.log('We are live on ' + port); });Now you should see the body as an object in the terminal.
现在你应该将 body 视为终端中的对象。
{ title: 'My Note Title', body: 'What a great note.' }
第一个路由的最后一步:设置数据库,然后添加数据。
最简单方法是通过mLab 设置 Mongo 数据库的:它是最小的而且是免费的,设置的速度非常快。
创建帐户和 MongoDB 部署后,将用户的用户名和密码添加到数据库:

然后复制这里第二个 URL:

在项目根目录的目录配置中,创建一个db.js文件。
mkdir config cd config touch db.js
在里面,添加刚才的URL:
module.exports = { url : YOUR URL HERE };别忘了把你的用户名和密码(来自数据库用户的密码,而不是你的 mLab 帐户)添加到URL中。 (如果你要将此项目提交到 Github 上,请确保包含 .gitignore 文件 像这样,,不要与任何人分享你的密码。)
现在在你的 server.js 中,可以用 MongoClient 连接到数据库了,使用它来包装你的应用程序设置:
// server.js const express = require('express'); const MongoClient = require('mongodb').MongoClient; const bodyParser = require('body-parser'); const db = require('./config/db'); const app = express(); const port = 8000; app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({ extended: true })); MongoClient.connect(db.url, (err, database) => { if (err) return console.log(err) require('./app/routes')(app, database); app.listen(port, () => { console.log('We are live on ' + port); }); })如果你用的是最新版本的 MongoDB(3.0+),请将其修改为:
// server.js const express = require('express'); const MongoClient = require('mongodb').MongoClient; const bodyParser = require('body-parser'); const db = require('./config/db'); const app = express(); const port = 8000; app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({ extended: true })); MongoClient.connect(db.url, (err, database) => { if (err) return console.log(err) // Make sure you add the database name and not the collection name const database = database.db("note-api") require('./app/routes')(app, database); app.listen(port, () => { console.log('We are live on ' + port); }); })这是你的基础架构的最后一个设置!
添加到你的数据库
MongoDB将数据存储在 collections 中。在你的项目中,你希望将笔记存储在一个名为 notes 的 collection 中。
由于将数据库作为路径中的 db 参数传入,因此可以像这样访问它:
db.collection('notes')创建笔记就像在集合上调用 insert 一样简单:
const note = { text: req.body.body, title: req.body.title} db.collection('notes').insert(note, (err, results) => { }插入完成后(或由于某种原因失败),要么返回错误或反回新创建的笔记对象。这是完整的 note_routes.js 代码:
// note_routes.js module.exports = function(app, db) { const collection = app.post('/notes', (req, res) => { const note = { text: req.body.body, title: req.body.title }; db.collection('notes').insert(note, (err, result) => { if (err) { res.send({ 'error': 'An error has occurred' }); } else { res.send(result.ops[0]); } }); }); };试试看!使用 Postman 发送 x-www-form-urlencoded POST 请求,在 Body 选项卡下设置 title 和 body。
响应应如下所示:

如果你登录mLab,你还应该能够在数据库中看到创建的笔记。
READ 路由
现在可以稍微加快步伐。
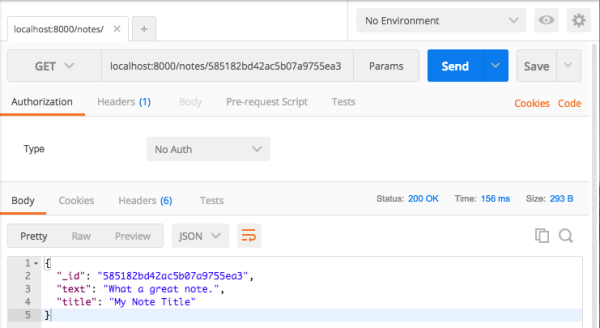
假设你希望通过导航到 localhost:8000/notes/{id} 来获取刚创建的笔记。这是链接应该是localhost:8000/notes/585182bd42ac5b07a9755ea3。(如果你没有得到其中笔记的 ID,可以通过检查 mLab 或创建一个新的笔记)。
以下是 note_routes.js 中的内容:
// note_routes.js module.exports = function(app, db) { app.get('/notes/:id', (req, res) => { }); app.post('/notes', (req, res) => { const note = { text: req.body.body, title: req.body.title }; db.collection('notes').insert(note, (err, result) => { if (err) { res.send({ 'error': 'An error has occurred' }); } else { res.send(result.ops[0]); } }); }); };就像以前一样,你将在数据库 collection 中调用一个方法。在这里,它被恰当地命名为 findOne。
// note_routes.js module.exports = function(app, db) { app.get('/notes/:id', (req, res) => { const details = { '_id': }; db.collection('notes').findOne(details, (err, item) => { if (err) { res.send({'error':'An error has occurred'}); } else { res.send(item); } }); }); app.post('/notes', (req, res) => { const note = { text: req.body.body, title: req.body.title }; db.collection('notes').insert(note, (err, result) => { if (err) { res.send({ 'error': 'An error has occurred' }); } else { res.send(result.ops[0]); } }); }); }; 你可以通过 req.params.id 从 URL 参数中获取 id。但是,如果你试图将字符串插入上面的
MongoDB 不仅要求 ID 为字符串,还要求 ID 是一个对象,它们被之为 ObjectID。
别担心,这很容易解决。这是完整的代码:
// note_routes.js var ObjectID = require('mongodb').ObjectID; module.exports = function(app, db) { app.get('/notes/:id', (req, res) => { const id = req.params.id; const details = { '_id': new ObjectID(id) }; db.collection('notes').findOne(details, (err, item) => { if (err) { res.send({'error':'An error has occurred'}); } else { res.send(item); } }); }); app.post('/notes', (req, res) => { const note = { text: req.body.body, title: req.body.title }; db.collection('notes').insert(note, (err, result) => { if (err) { res.send({ 'error': 'An error has occurred' }); } else { res.send(result.ops[0]); } }); }); };尝试使用一个笔记 ID,它应如下所示:
DELETE 路由
实际上删除对象与查找对象几乎相同。你只需用 remove 函数替换 findOne 即可。这是完整的代码:
// note_routes.js // ... app.delete('/notes/:id', (req, res) => { const id = req.params.id; const details = { '_id': new ObjectID(id) }; db.collection('notes').remove(details, (err, item) => { if (err) { res.send({'error':'An error has occurred'}); } else { res.send('Note ' + id + ' deleted!'); } }); }); // ...UPDATE 路由
最后一个! PUT 方法基本上是 READ 和 CREATE 的混合体。你找到该对象,然后更新它。如果刚才你删除了数据库中唯一的笔记,那就再创建一个!
代码:
// note_routes.js // ... app.put('/notes/:id', (req, res) => { const id = req.params.id; const details = { '_id': new ObjectID(id) }; const note = { text: req.body.body, title: req.body.title }; db.collection('notes').update(details, note, (err, result) => { if (err) { res.send({'error':'An error has occurred'}); } else { res.send(note); } }); }); // ...现在你可以更新任何笔记,如下所示:

请注意这些代码还不完美 ―― 比如你没有提供正文或标题,PUT 请求将会使数据库中的笔记上的那些字段无效。
API 完成
就这么简单!你完成了可以进行 CRUD 操作的 Node API。
本教程的目的是让你熟悉 Express、Node 和 MongoDB ―― 你可以用简单的程序作为进军更复杂项目的跳板。
以上就是30分钟用Node.js构建一个API服务器的步骤详解的详细内容,更多请关注0133技术站其它相关文章!








