这篇文章主要介绍了浅谈web服务器项目中静态请求和动态请求处理,文中通过示例代码介绍的非常详细,对大家的学习或者工作具有一定的参考学习价值,需要的朋友们下面随着小编来一起学习学习吧
注:完整项目下载
在处理了核心任务之后,我们会发现有些请求并不是都是静态的,那么我们就需要进行实现处理动态请求的要求,如下面代码是我们请求的解决方式,我们只需在HttpRequestImpl实现类中,将如下代码实现具体的判断过程
//判断当前请求的否是静态资源 public boolean isStaticResource(){ return true; } //判断当前请求的否是动态资源 public boolean isDynamicResource(){ return true; }1、实现isStaticResource()方法:
// 判断当前请求的否是静态资源 public boolean isStaticResource() { // 存在??文件??静态?? System.out.println("进入isStaticResource()方法"); if (requestPath != null) { String parent = ConfigUtils.getConfigValue("rootPath"); File file = new File(parent, requestPath); return file.exists() && file.isFile(); } return false; } 2、实现isDynamicResource():
// 判断当前请求的否是动态资源 public boolean isDynamicResource() { // 存在??文件??动态?? System.out.println("进入isDynamicResource()方法"); String path = ServletMappingUtils.getMappingValue(requestPath); /* * //使用路径判断,当时我不知道还有一个叫做isContains(key)的方法,如果知道的话 就可以使用了,请参见测试类 * if(isContainers(requestPath())) { return *; } */ System.out.println("ServletMapping中根据requestPath获取的映射:" + path); if (path != null) { return true; } return false; } 在动态方法中,我们String path = ServletMappingUtils.getMappingValue(requestPath);来获取请求的资源的路径,如果存在值的话就返回结果,其实现如下所示,对于servlet_mapping.properties文件,还是复制到项目下即可:
package com.sample.utils; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.util.Properties; public class ServletMappingUtils { private static Properties p; static { InputStream in=null; p=new Properties(); try { //读了xx.properties文件 in=ServletMappingUtils.class.getResourceAsStream("servlet_mapping.properties"); //放置到p中,即放properties文件中的key,value p.load(in); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if(in!=null) try { in.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } public static String getMappingValue(String mapping) { return p.getProperty(mapping); } public static boolean isContainsKey(String key) { return p.containsKey(key); } public static void main(String[] args) {//输出测试 // Properties p=new Properties(); // p.setProperty("rootPath","ddd"); // System.out.println(p.get("rootPath")); System.out.println(getMappingValue("/HelloWorld")); System.out.println(isContainsKey("/Login")); } } 3、实现对静态请求和动态请求的封装
在处理完基本的功能性要求之后,我们实现对核心任务取得封装,在封装时,我们仍然采用类实现接口的方式,首先我们需要明确该确定一个怎么样的接口,其代码如下:
package com.sample.http; //Http资源处理器 //负责处理http协议的资源请求 public interface HttpAccessProcessor { //处理静态资源 页面/文件/图片等等 public void processStaticResource(HttpRequest request,HttpResponse response); //处理动态资源 java代码 浏览器通过路径发送请求可以访问调用java代码 public void processDynamicResource(HttpRequest request,HttpResponse response); //向浏览器返回错误信息及其页面 public void sendError(int statusCode,HttpRequest request,HttpResponse response); } 其实现类如下所示:
package com.sample.http; import com.sample.utils.ServletMappingUtils; //Http资源处理器 //负责处理http协议的资源请求 public class HttpAccessProcessorImpl implements HttpAccessProcessor { //处理静态资源 页面/文件/图片等等 public void processStaticResource(HttpRequest request,HttpResponse response) { System.out.println("进入方法processStaticResource(HttpRequest request,HttpResponse response)"); //获取请求中资源,并处理 String path=request.getRequestPath(); String[] str=path.split("[.]"); String contentType=str[str.length-1]; System.out.println("路径的后缀:"+contentType); response.setStatusLine(200); response.setContentType(MIMEUtils.getMimeValue(contentType)); response.setCRLF(); response.printResponseHeader(); response.printResponseContent(request.getRequestPath()); } //处理动态资源 java代码 浏览器通过路径发送请求可以访问调用java代码 public void processDynamicResource(HttpRequest request,HttpResponse response) { System.out.println("进入processDynamicResource"); response.setStatusLine(200); response.setContentType("text/HTML"); response.setCRLF(); response.printResponseHeader(); Class className=null; try { String path=ServletMappingUtils.getMappingValue(request.getRequestPath()); System.out.println("使用反射获取的servlet路径:"+path); className = (Class.forName(path)); //ServletImpl servlet= (ServletImpl) className.newInstance(); Servlet servlet = (Servlet) className.newInstance(); System.out.println(servlet); servlet.service(request, response); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (InstantiationException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } //向浏览器返回错误信息及其页面 public void sendError(int statusCode,HttpRequest request,HttpResponse response) { System.out.println("进入sendError()"); //获取请求中资源,并处理 //response.setStatusLine("OK"); response.setStatusLine(statusCode); //response.setStatusLine("OK"); response.setContentType("text/html"); response.setCRLF(); response.printResponseHeader(); //response.printResponseContent("/error/404.html"); response.printResponseContent(ErrorPageUtils.getErrorPage(statusCode+"")); } } 同样的,在写完代码之后,在response.setContentType(MIMEUtils.getMimeValue(contentType));String path=ServletMappingUtils.getMappingValue(request.getRequestPath());response.printResponseContent(ErrorPageUtils.getErrorPage(statusCode+""));出现问题,按照以前编写的代码进行处理即可,在设置ServletMappingUtils.getMappingValue(request.getRequestPath())部分时,我们要将文件的配置路径设置为自己的类所在的包下面,比如我们的Servlet实现类在com.sample.servlet.HelloWorldServlet,则应该写为/HelloWorld=com.sample.servlet.HelloWorldServlet。
值得注意的是Servlet servlet = (Servlet) className.newInstance();处的错误信息,在这里我们需要再创建一个类进行处理动态跳转,如下所示:
package com.sample.servlet; import com.sample.http.HttpRequest; import com.sample.http.HttpResponse; //只有实现这个接口的类,才可以被浏览器发送请求访问到 public interface Servlet { //被浏览器发请求访问到的对象会调用这个指定方法service,进行处理这次浏览器的请求 public void service(HttpRequest request,HttpResponse response); } 下面是实现类HelloWorldServlet,其代码如下所示:
package com.sample.servlet; import java.io.PrintWriter; import com.sample.http.HttpRequest; import com.sample.http.HttpResponse; //只有实现这个接口的类,才可以被浏览器发送请求访问到 public class HelloWorldServlet implements Servlet{ //被浏览器发请求访问到的对象会调用这个指定方法service,进行处理这次浏览器的请求 public void service(HttpRequest request,HttpResponse response) { String name=request.getParameter("name"); System.out.println(name); try { PrintWriter pw=response.getPrintWriter(); pw.println(""); pw.println(""); pw.println(""+name+":这是我的Servlet "); pw.println(""); pw.println(""); pw.flush(); pw.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } 这样就完成了动态跳转页面,但是,我们在每次创建是都需要来new一个新对象,这样不仅浪费时间空间内存等等,最重要的用户体验都找不见了,那么我们就对其再次进行封装,其代码如下,实现request,response对象的封装:
package com.sample.http; //负责创建http协议访问过程中使用到的对象 public interface HttpCreator { //返回创建好的request对象 public HttpRequest getHttpRequest(); //返回创建好的response对象 public HttpResponse getHttpResponse(); //返回创建好的HttpAccessProcessor对象 public HttpAccessProcessor getHttpAccessProcessor(); } 下面就是实现类:
package com.sample.http; import java.net.Socket; //负责创建http协议访问过程中使用到的对象 public class HttpCreatorImpl implements HttpCreator{ private Socket s; HttpRequestImpl request; HttpResponseImpl response; HttpAccessProcessorImpl hapi; public HttpCreatorImpl(Socket s) { this.s=s; } //返回创建好的request对象 public HttpRequest getHttpRequest() { return request=new HttpRequestImpl(s); } //返回创建好的response对象 public HttpResponse getHttpResponse() { return response=new HttpResponseImpl(s); } //返回创建好的HttpAccessProcessor对象 public HttpAccessProcessor getHttpAccessProcessor() { return hapi=new HttpAccessProcessorImpl(); } } 到此,我们完成了所有对象的封装,下面我们进行测试,写测试类如下所示:
package com.sample.http; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.ServerSocket; import java.net.Socket; public class ServerTest { public static void main(String[] args) { //声明变量 ServerSocket ss=null; Socket s=null; boolean flag=true; try { int port=10002; System.out.println("Server Port:"+port); ss=new ServerSocket(port); //while(flag) { //接受客户端发送过来的Socket s=ss.accept(); HttpCreatorImpl hci=new HttpCreatorImpl(s); HttpRequest request=hci.getHttpRequest(); HttpResponse response=hci.getHttpResponse(); HttpAccessProcessor hapi=hci.getHttpAccessProcessor(); // 用于测试收到的信息 if(request.isStaticResource())//处理静态信息 { hapi.processStaticResource(request, response); } else if(request.isDynamicResource())//处理动态请求 { hapi.processDynamicResource(request, response); } else//无法处理时 { System.out.println("无法处理"); hapi.sendError(404, request, response); } } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } 当我们在浏览器中输入http://127.0.0.1:10002/HelloWorld?id=1212&name=suguniang信息回车时能够看到如下所示界面,但是此时的状态是在项目文件夹webapps中根本不存在HelloWorld页面,但是我们能够正常访问到页面信息,而此时返回的信息正是我们的Servlet实现类中的内容:
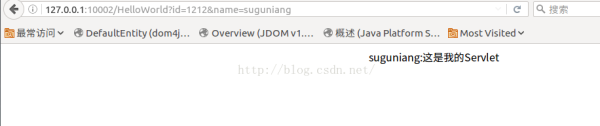
而当我们在URL中输入不存在的请求资源时,则会弹出404界面
到此这篇关于浅谈web服务器项目中静态请求和动态请求处理的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关web服务器中静态请求和动态请求内容请搜索html中文网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持html中文网!
以上就是浅谈web服务器项目中静态请求和动态请求处理的详细内容,更多请关注0133技术站其它相关文章!







